What Investors Should Know About New Fed Leadership
The Federal Reserve (often called "the Fed") helps manage the U.S. economy and financial system. In May 2026, Jerome Powell's time as Fed Chair ends. This means the president will choose a new leader for the Fed, which could affect interest rates and investment markets.
News headlines often talk about whether the Fed will raise or lower interest rates. But there's a bigger question: What should the Fed's job actually be? The Fed's responsibilities have grown over the years, and people disagree about how much power it should have. These debates matter because they shape both current decisions and the Fed's future role.
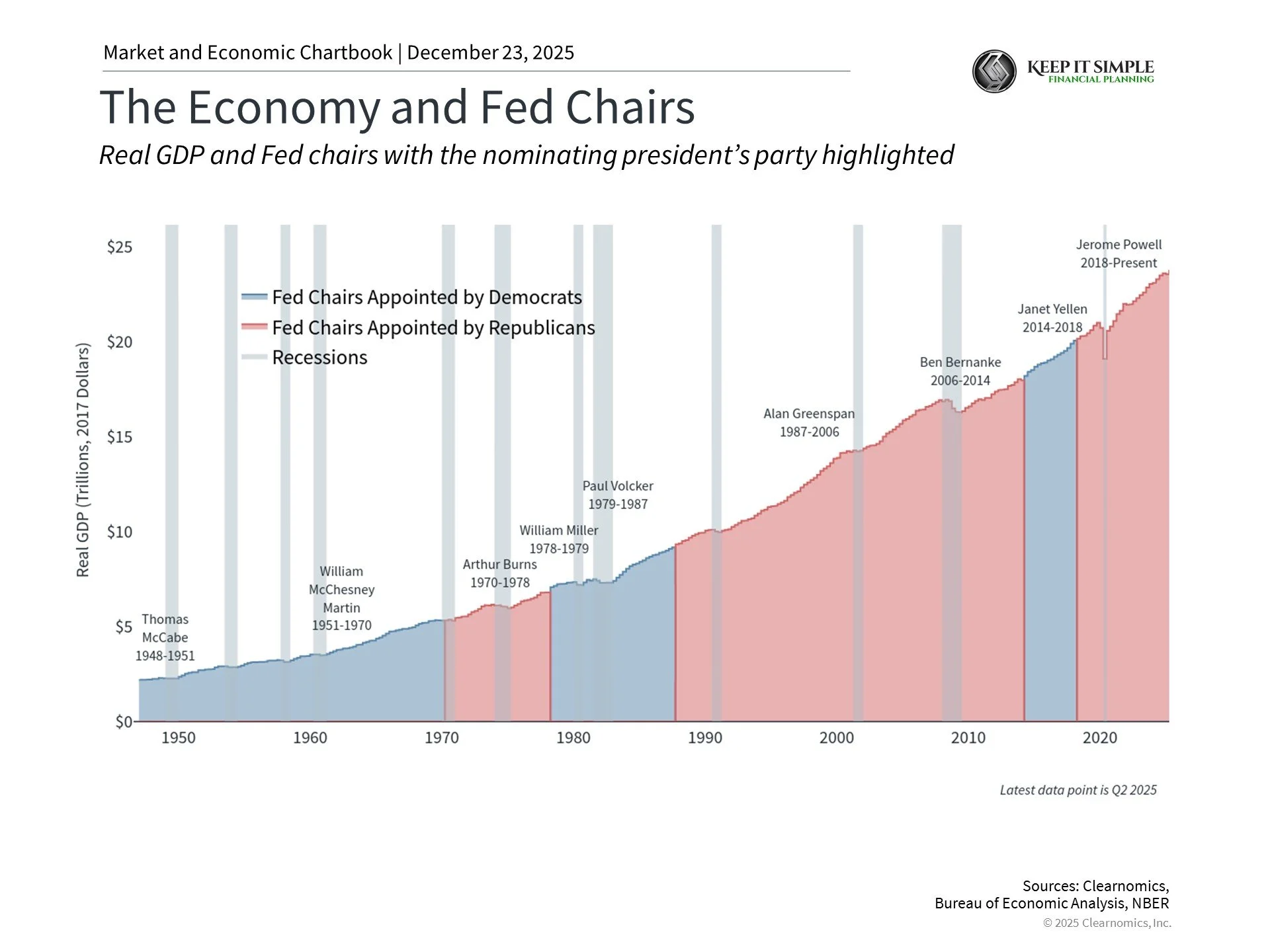
The Fed's job has grown over time
Congress created the Federal Reserve in 1913 to prevent bank panics. In the 1800s and early 1900s, these panics happened when people rushed to take money out of banks all at once. This could cause banks to fail and hurt the whole economy.
Today, the Fed still protects the banking system. It acts as a "lender of last resort," meaning it steps in during financial emergencies. Just knowing the Fed is there helps keep the system stable.
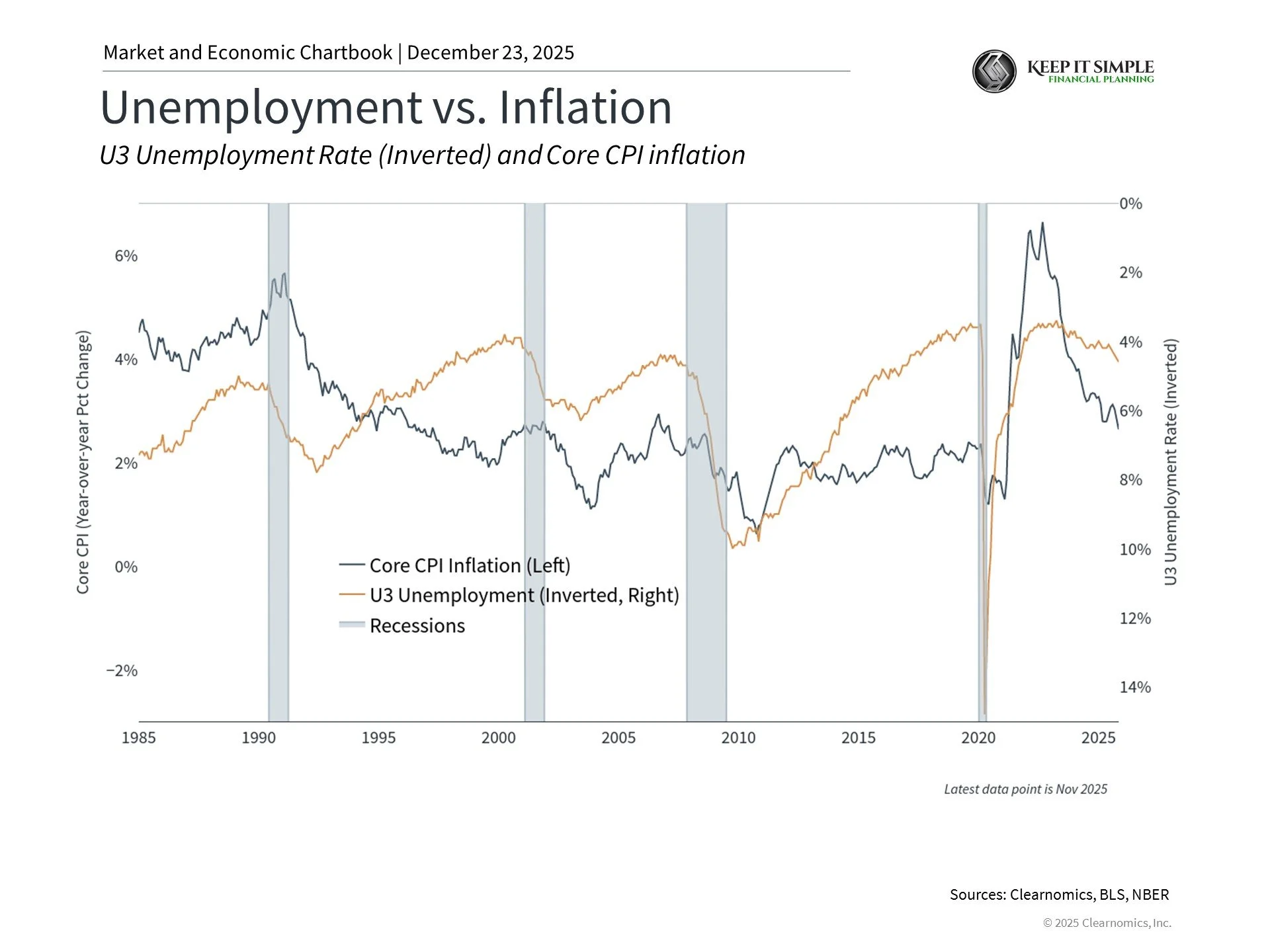
But the Fed's job expanded in 1977. Congress told it to focus on three goals: full employment, stable prices (meaning low inflation), and moderate interest rates. The Fed usually focuses on the first two goals, which it calls its "dual mandate."
This is why people pay so much attention to Fed interest rate decisions. The Fed now manages not just banks, but the whole economy. This expanded role is sometimes called "mission creep."
Fed independence has pros and cons
The president chooses Fed officials and Congress approves them, but voters don't elect them directly. Some people think this gives too much power to unelected officials. Others say the Fed needs independence to make tough choices that help the economy long-term, even if they're unpopular short-term.
In the 1970s and early 1980s, the U.S. had both high inflation and high unemployment at the same time. Fed Chair Paul Volcker raised interest rates sharply, which caused a recession but eventually fixed the problem. This showed why Fed independence can be important.
The Fed doesn't always get things right. It made mistakes during the Great Depression. More recently, some think it was slow to respond to inflation that started in 2021. The Fed mainly controls short-term interest rates, but this is a limited tool. It can't fix supply chain problems, trade issues, or other complex economic challenges.
New leadership in 2026
The White House will likely name a new Fed Chair early in 2026. Current top candidates include Kevin Warsh and Kevin Hassett, though this could change.
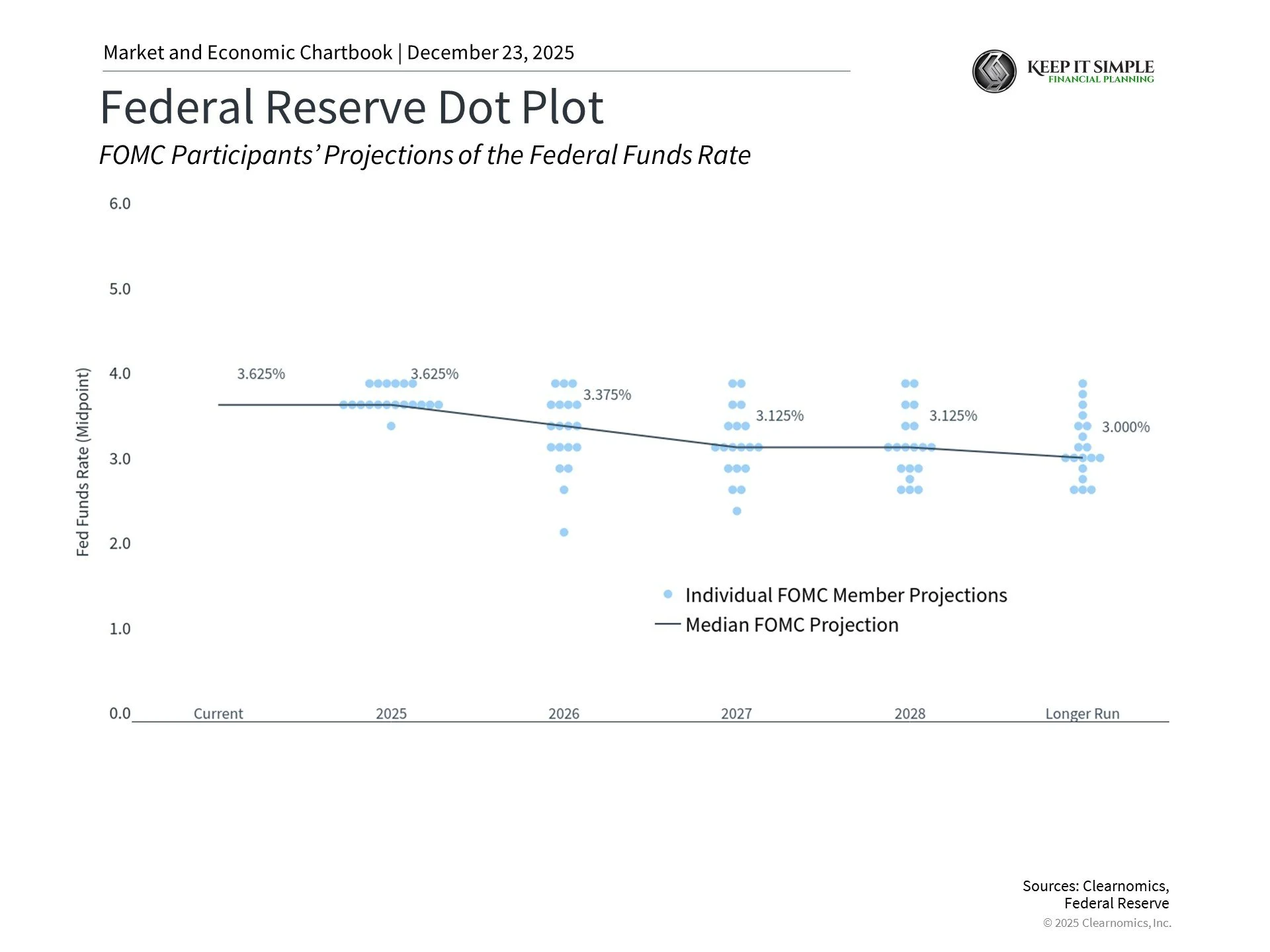
The chart above shows Fed projections for interest rates. The Fed may cut rates once in 2026 and once in 2027. The next Fed Chair will likely favor lower rates, which could change these projections.
However, the Fed Chair is just one voice. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) has twelve voting members who make decisions together. The Fed tries to reach agreement among these members.
It's worth remembering that the economy has grown steadily under different Fed Chairs from both political parties. President Trump nominated Jerome Powell during his first term, and Powell continued under President Biden. What matters most is whether Fed policy fits economic conditions, not who leads the Fed.
While news about Fed leadership will continue, the overall health of the economy matters more than any single Fed decision. The next Fed Chair may prefer lower rates, but this will depend on jobs and inflation. For investors, it's best to stick with a plan that matches your financial goals rather than react to daily Fed news.
The bottom line? Markets have done well under different Fed Chairs and policies. For investors, focusing on long-term goals remains the best approach.
Want to learn how Keep It Simple Financial Planning can help? Please don’t hesitate to reach out here.